Before jumping head-first into crypto like so many people do, you have to understand the key differences between a crypto exchange and a wallet. They’re both important tools—but do very different things. Crypto exchanges help you buy, sell, and trade digital assets. Crypto wallets are where you keep those precious assets safe.
Knowing how each works can help you avoid rookie mistakes and make smarter moves.
Table of Contents
Why Understanding the Difference Matters
When you’re choosing between a crypto exchange and a wallet, you aren’t just picking whatever looks prettiest. It’s about walking the fine balance between control and risk. Exchanges are built for buying, selling and trading digital assets, and wallets are built for securely storing your crypto. Confusing the two can lead to lost funds or missed opportunities.
Leave your assets on an exchange, and there’s a chance (even if it’s a small one) that it could get hacked, leaving you with nothing. But store your crypto on a cold wallet that doesn’t support swaps, and you’ll miss out on big plays and major price movements.
How Is a Cryptocurrency Exchange Different from a Cryptocurrency Wallet?
People use cryptocurrency exchanges to buy, sell and trade digital assets, but a crypto wallet is where they shelf those assets for long-term storage—this is the key difference.
Exchanges handle transactions, set pricing, and match market orders between users. But wallets don’t usually let you trade directly. Instead, they just store your private keys and allow you to send or receive crypto securely, without having to rely on a third party.
Exchanges are for action, wallets are for stability. You trade on exchanges, but you protect your crypto in a wallet.
What Is a Cryptocurrency Exchange?
Simply put, a cryptocurrency exchange is a platform that lets you buy, sell and trade crypto. You’ll also be able to convert fiat currencies like USD into crypto, or crypto back into fiat.
In general, you’ll hear two main types of crypto exchange talked about in any crypto spaces: they’re centralized exchanges (CEX) and decentralized exchanges (DEX). CEXs are usually run by classic, real-world companies, require ID verification, and offer customer support. Meanwhile, DEXs let you trade directly with others using smart contracts—no middlemen involved.
A lot of crypto exchanges will also have useful extra tools like price charts, staking, and margin trading. But keep in mind that storing crypto on an exchange for long periods of time comes with some risks.
What Is a Crypto Wallet?
A crypto wallet is an address which can securely store, send, and receive crypto. This enables users to manage their digital assets, public and private keys in an easy-to-use way, all in one place without risking security. There are several types of crypto wallets:
Software wallets can be mobile apps, browser extensions or even desktop wallets that you can install directly on your computer. Meanwhile hardware wallets offer stronger security, since they store assets entirely offline. There are also paper wallets, which are basically just keys printed out on paper, like the name suggests. They’re definitely safe from online attacks, but you wouldn’t want your cat playing with one.
There’s also the option of choosing custodial or non-custodial wallets. One allows a company to hold your keys for you, and the other gives control entirely to you.
Just remember: for long-term holding, use a hardware wallet. For active use, go with a software wallet like MetaMask or Trust Wallet.

Key Differences Between Exchanges and Wallets
Exchanges vs wallets serve different roles in the world of crypto. Exchanges are used to buy, sell and trade cryptocurrencies, and wallets are used to store them.
Ownership and Control of Funds
A centralized crypto exchange ultimately has control of both user funds and private keys. But on a decentralized exchange, you can trade directly from your own wallet.
A crypto wallet gives you full ownership and control of all your assets. This is especially true of non-custodial wallets. You’re able to manage all your private keys yourself, and no third parties can access them without your knowledge and consent.
Security Features and Risks
Crypto exchanges are often targeted by hackers because they store a lot of user funds. Watch out, because if an exchange is breached, your crypto could be in serious danger.
This is a far cry from crypto wallets, which provide more enhanced security and control when compared to even the most secure exchanges. With a wallet, you manage your private keys yourself, and there’s a much lower chance you’ll be hacked or become a victim of mismanagement.
Hardware wallets, for instance, store keys offline, safeguarding assets from online threats. This is why, even though exchanges definitely offer more convenience for trading, wallets are still preferable for long-term storage and security.
Access to Private Keys
If you’re planning to use an exchange to store your digital currency, you should be aware that you won’t have access to the private keys that control your funds. The platform holds them on your behalf. This means you have to rely on its security systems and policies.
But if you have a cold, non-custodial crypto wallet, you can keep your private keys offline. This gives you complete control of your digital assets and eliminates extra risk. Keeping your private keys offline is an extremely effective way to protect your assets from theft or loss.
Use Cases
Crypto exchanges are best for active trading. They let you buy, sell, or swap crypto assets quickly. They can also check prices, and access real-time markets. If you need trading pairs, liquidity, or fiat conversion, an exchange is the way to go.
Crypto wallets are for secure storage and holding digital assets long-term. They give you full control of your crypto, especially with a cold wallet that keeps keys offline. Wallets are also important for using dApps, staking, or simply keeping your crypto safe.
Read more: The Top 10 dApps You Should Know About
Connectivity
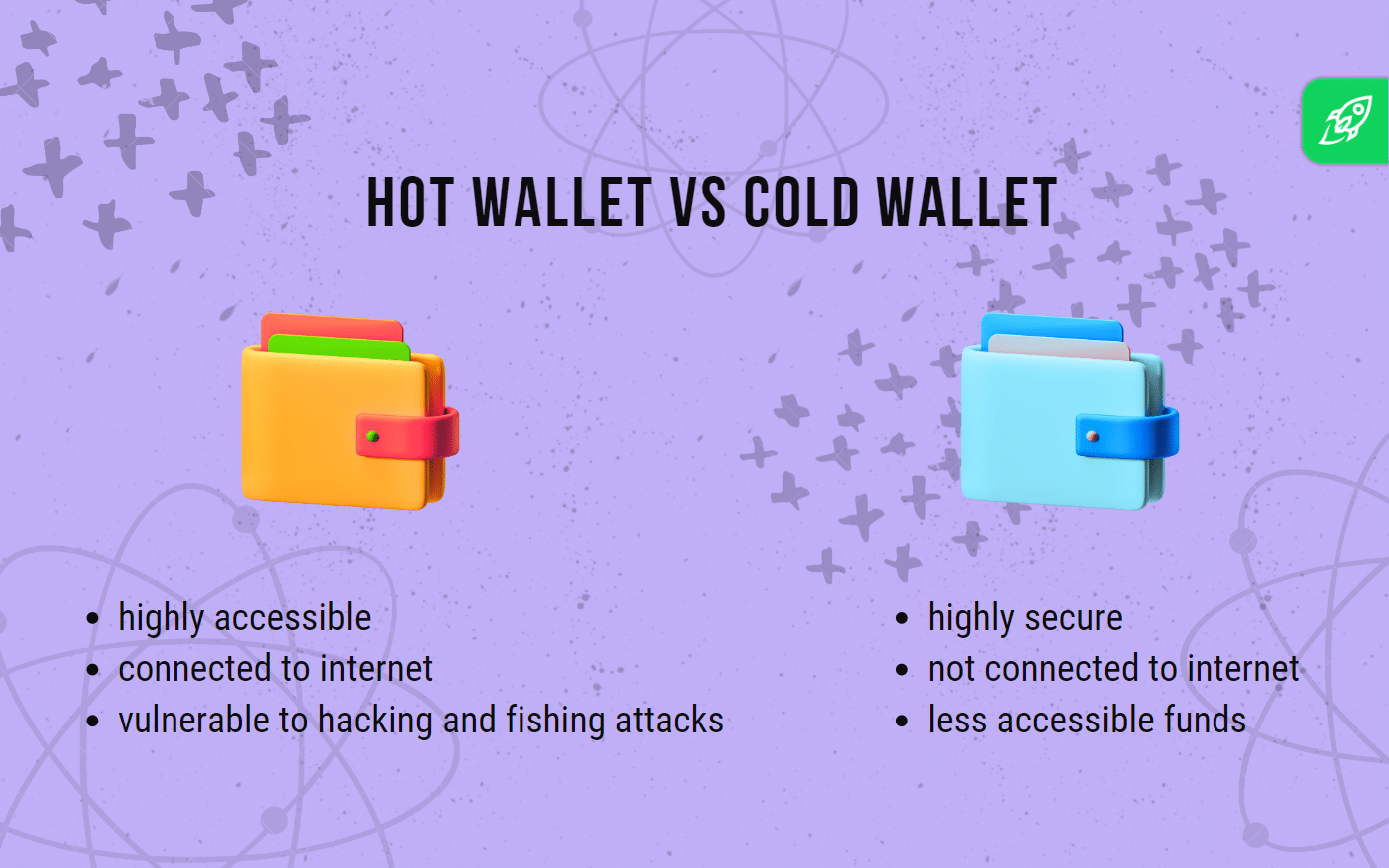
Crypto exchanges are always online, giving you instant access to buy, sell, and react to market changes. That’s great for active trading—but it also means they’re more exposed to hacks and scams, since they’re always online.
For example, the exchange Bybit lost over $1.5 billion in ETH after hackers exploited a wallet transfer. They compromised a developer’s device and quietly rerouted the funds. Even major platforms face risks like this. This is why many users trade on exchanges, but still choose to store their crypto elsewhere.The safest crypto wallets are cold wallets, which stay offline for better security. Hot wallets, however, are online and therefore easier to access. You should choose between all these options based on how often you need to use your crypto and how risky you want your moves to be.
User Experience
Crypto exchanges feel familiar—like using a bank account or a trading app. You can also deposit fiat currency to buy crypto directly, making exchanges the main entry point for most beginners.
Crypto wallets vary in user experience. Using paper wallets is as easy as printing out a piece of paper with your keys. Mobile and online wallets take some getting used to. Hardware wallets offer more security but require extra steps.
Though wallets need more setup, they give you full control and direct access to your crypto.
Fees
Crypto exchanges charge fees for trading, withdrawing, and deposits. Costs vary by platform, trade size, and payment method. Some offer tiered pricing, with lower fees for high-volume users.
Crypto wallets don’t usually charge platform fees, but network fees still apply. These vary by blockchain and are required to process transactions.
Regulation & KYC
When it comes to crypto exchanges, they usually require you to pass Know Your Customer (KYC) checks before you can make any crypto transactions. You’ll have to verify your identity with a photo ID or other personal info to pass one of these checks. This helps the company prevent fraud and comply with anti money-laundering laws.
Crypto wallets don’t typically require KYC, though. You can create a wallet for storing digital assets without revealing your identity. This definitely offers you more privacy, but comes at the cost of fewer legal protections if something goes wrong.
Backup & Recovery
Crypto exchanges handle backups for you. If you forget your password, you can reset it using your email and ID. But the platform controls your access.
Crypto wallets leave recovery up to you. You get a recovery phrase that restores your wallet. Lose it, and you lose all your digital money. There’s no way to reset.
Integration with Services
Crypto exchanges connect easily with banks, payment apps, and trading tools, enabling users to buy crypto with a card, move user funds fast, and use built-in features like charts and order books.
Crypto wallets link with dApps, NFT platforms, and DeFi protocols. Many let you swap tokens, stake assets, or play blockchain games without leaving the app.
Anonymity
Crypto exchanges require you to submit documents to verify your identity. This is called KYC. This way, you’ll be able to trade, withdraw, or access your digital assets. This process helps meet legal standards but limits your privacy.
Crypto wallets don’t ask for your identity. You can send, receive, and manage crypto without linking it to your personal information. This makes wallets more private—but also places more responsibility on you to stay secure.
Crypto Exchange vs. Wallet: Comparison Table
Should You Use an Exchange, a Wallet, or Both?
If you’re new to crypto, a crypto exchange is the easiest place to start. You can buy, sell, and swap digital assets quickly through a user-friendly platform. But exchanges aren’t built for long-term storage. Centralized exchanges hold your private keys—so if the platform is hacked or goes offline, your funds could be lost.
Cryptocurrency wallets give you full control over your assets. They’re better for long-term storage and offer more security. Non-custodial wallets also let you interact directly with decentralized applications (dApps), such as DeFi platforms and NFT marketplaces.
For most users, the smart move is to use both crypto exchanges and wallets. Use the exchange for trading and conversions, and your wallet to safely store assets and access dApps. It’s the best way to balance convenience with control.
Common Beginner Mistakes to Avoid
- Leaving Funds on an Exchange
Sure, keeping your crypto on a centralized exchange is definitely convenient, but it actually exposes you to some significant risks. A lot can go wrong with centralized systems. Exchanges can go offline, get hacked, or freeze withdrawals, leaving your funds lost somewhere on the blockchain. Storing your assets on a hardware wallet is your best bet in terms of security.
- Forgetting Seed Phrases or Passwords
This is important: If you lose your seed phrase or password after setting up your crypto wallet, you can lose your access to it permanently. On top of that, forgetting even one word of your seed phrase can make it completely useless.
- Falling for Phishing Scams
If you’ve heard of phishing scams you already know that they use fake websites or emails to mimic legit crypto services and try to steal your assets. You might even think you’ll be able to recognize one of these scams if you’re the one being scammed. But don’t be so sure. Crypto is often targeted by phishing scams, and attackers will go to very great lengths just to get you to give them your wallet address and everything on it.
How to Move Crypto Off an Exchange and Store Coins on a Wallet
1. Setting Up Your First Wallet
Start by choosing a wallet—software wallets are easy to use, while hardware wallets offer more protection. Follow the setup instructions and save your wallet address for future transfers.
2. Basic Security Tips
Make sure you’ve got two-factor authentication (2FA) enabled to protect your funds. Write down your recovery phrase and store it somewhere safe, offline. If you lose this phrase, you lose your crypto.
3. Storing Coins on Your Wallet with Changelly
Once your crypto wallet is ready, you can buy or swap crypto on Changelly and send it directly to your wallet address. It works a lot like transferring money to a bank account—simple, safe, and familiar. Changelly supports hundreds of trading pairs and makes managing assets easy, even for beginners.

Final words
There are crucial differences you need to know to make the choice between crypto exchange vs crypto wallet. Crypto exchanges are for trading, crypto wallets for storing. To stay safe, avoid common mistakes and secure your digital assets. Whether you’re starting out or building a portfolio, always know where your crypto is and who controls it.
FAQ
Can I store my crypto on an exchange forever?
Yes, but it’s not very safe. While both crypto exchanges and wallets are both vulnerable to hacking, exchanges (especially centralized exchanges) are much more likely to be hacked, and can go offline entirely. For long-term storage, cryptocurrency wallets are the safer way to store crypto.
Do I need a wallet to buy cryptocurrency?
No, you can buy crypto directly on an exchange. But you’ll definitely need a crypto wallet if you want full control of your assets, or if you plan to move them anywhere off the platform.
What happens if I lose access to my wallet or exchange account?
If you lose your access to the wallet where you store your funds, and don’t have (or don’t remember) your recovery phrase, all your crypto is basically gone. But if you’re facing the same problem with an exchange, you can usually recover your access with ID verification.
Are crypto wallets free to use?
Yes, most crypto wallets are free—but it depends on the type. Software, mobile and web wallets are usually free to download and use. Hardware wallets, like Ledger or Trezor, must be purchased. No matter the type, you’ll still pay network fees when sending or swapping crypto.
Is a mobile wallet safe for beginners?
Yes! But you have to keep it secure. Make sure to use a wallet that’s trusted by the community, set a strong password, use 2FA, and back up your recovery phrase.
What’s better for a beginner—using an exchange or a wallet?
Both are useful, but for different reasons. Exchanges are better for getting started, buying, selling, and trading. Wallets give you more control and security. In the long run, it’s best to use both—an exchange for transactions, and a wallet as a secure storage solution.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.